Solar power systems are more than just panels. The right accessories can dramatically improve efficiency, extend system life, and provide peace of mind.
Whether you’re a seasoned solar enthusiast or just starting your renewable energy journey, this guide will help you navigate the world of solar accessories.
With the growing popularity of renewable energy, understanding how to optimize your solar setup has never been more important.
Understanding the Solar Ecosystem
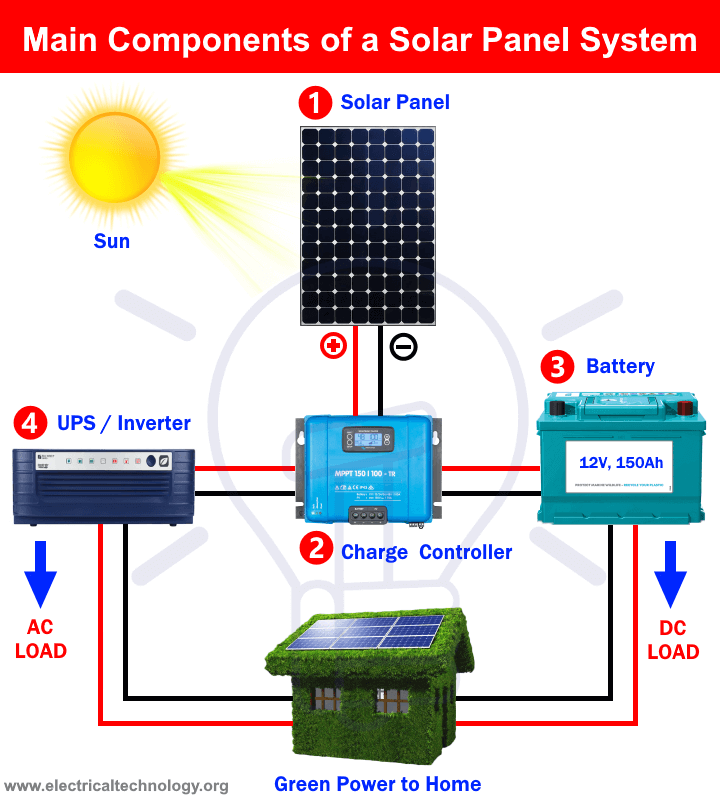
Before diving into specific accessories, it’s helpful to understand how a complete solar system works.
A basic setup includes:
- Solar panels – Capture sunlight and convert it to electricity
- Mounting hardware – Secures panels to your roof or ground
- Inverters – Convert DC electricity from panels to AC for home use
- Electrical connections – Transfer power throughout the system
The accessories we’ll discuss enhance this basic framework, adding functionality, efficiency, and protection.
Essential Solar Accessories for Every System
Monitoring Equipment
One of the most valuable additions to any solar setup is a good monitoring system.
These devices track your system’s performance in real-time, helping you:
- Identify performance issues before they become problems
- Understand your energy production patterns
- Track your return on investment
- Detect faulty equipment or connections
- Create reports for warranty claims if needed
Many monitoring systems offer smartphone apps that let you check your solar production from anywhere.
Some advanced options even predict performance based on weather forecasts.
Types of Monitoring Systems:
- Panel-level monitors – Track individual panel performance
- System-level monitors – Track overall system output
- Consumption monitors – Track both production and home energy use
For those serious about optimizing their system, consumption monitors provide the most complete picture.
They show not just what you’re producing, but how it aligns with your usage patterns.
This data helps you schedule high-energy activities during peak production times.
Batteries: Store Now, Use Later
Solar batteries have transformed how we use solar energy. Instead of sending excess power back to the grid, you can:
- Store energy for nighttime use
- Maintain power during outages
- Reduce dependence on utility companies
- Take advantage of time-of-use billing by using stored power during peak rate hours
- Support critical systems during emergencies
Popular options include lithium-ion, lead-acid, and saltwater batteries.
Each type offers different benefits regarding lifespan, depth of discharge, and cost.
Charge Controllers: Protecting Your Investment
Charge controllers prevent battery damage by regulating the voltage and current coming from your solar panels.
The two main types are:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) – More affordable but less efficient
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) – More expensive but can increase energy harvest by 15-30%
For small systems, PWM controllers might be sufficient. For larger setups or when maximum efficiency matters, MPPT controllers are worth the extra cost.
MPPT controllers are particularly valuable in cooler climates or situations where panel voltage is significantly higher than battery voltage.
They can convert excess voltage into additional amperage, increasing overall power harvest.
Beyond basic regulation, modern charge controllers often include:
- Battery temperature compensation
- Multiple charging stages for battery health
- Data logging capabilities
- Remote monitoring options
- Programmable settings for different battery types
Expanding Your System’s Capabilities
Inverters: Converting DC to AC
Inverters transform the direct current (DC) from your panels into alternating current (AC) needed for household appliances.
Your options include:
- String inverters – Connect multiple panels to one inverter
- Microinverters – Attach to individual panels for better performance when shading is an issue
- Hybrid inverters – Work with batteries for energy storage
- Power optimizers – Pair with string inverters to improve individual panel performance
The right choice depends on your system size, budget, and specific needs.
String Inverters are the traditional choice and typically the most affordable option. They work well when all panels receive similar amounts of sunlight.
However, if some panels are shaded or face different directions, the entire string’s performance can be reduced to match the lowest-performing panel.
Microinverters address this limitation by converting DC to AC at each individual panel. If one panel is shaded, only that panel’s production is affected.
Microinverters also make it easier to expand your system later and provide panel-level monitoring. The downside is higher initial cost.
Hybrid Inverters combine standard inverter functionality with a battery charge controller. These are becoming increasingly popular as more homeowners add battery storage to their systems.
If you plan to add batteries in the future, a hybrid inverter can simplify the process.
Power Optimizers offer a middle ground between string inverters and microinverters.
They condition the DC electricity at each panel before sending it to a central string inverter, improving performance when panels are partially shaded or facing different directions.
Solar Panel Mounts
Mounting systems secure your panels and position them for optimal sunlight exposure:
- Fixed roof mounts – Most common residential option, attaches directly to roof
- Fixed ground mounts – Installed on the ground, easier to access for maintenance
- Pole mounts – Elevated installations that work well in areas with snow or flooding
- Adjustable mounts – Allow seasonal angle adjustments
- Tracking systems – Automatically follow the sun throughout the day
Tracking systems can increase energy production by 25-45% but require more maintenance and come at a higher cost.
Fixed Roof Mounts come in several varieties:
- Rail-based systems – Traditional approach with horizontal rails attached to roof
- Rail-less systems – Panels attach directly to mounting hardware, reducing materials and cost
- Shared-rail systems – Panels share rails along their edges, reducing material needs
- Ballasted systems – Use weight instead of roof penetrations, ideal for flat roofs
Ground Mounting Options offer advantages for properties with limited roof space or unfavorable roof orientation:
- Easier access for cleaning and maintenance
- Optimal angle and orientation regardless of roof structure
- Ability to add more panels than roof might accommodate
- Option to install panels over parking areas, creating covered spaces
Solar Panel Cleaners and Maintenance Kits
Regular cleaning can improve panel efficiency by up to 15%. A good maintenance kit typically includes:
- Extendable handles with soft brushes
- Non-abrasive cleaning solutions
- Squeegees for streak-free drying
- Safety harnesses for roof-mounted systems
- Inspection tools like multimeters for electrical testing
Safe Cleaning Practices Morning or evening cleaning prevents rapid evaporation and water spots. Always avoid:
- Metal brushes or abrasive materials
- High-pressure washers
- Harsh chemicals
- Hot water on cold panels (can cause cracking)
For systems on high or steep roofs, professional cleaning services might be the safest option. Many solar companies offer annual cleaning and inspection packages.
Smart Home Integration
Solar-Compatible Smart Home Devices
Modern solar systems can work with smart home technology to maximize energy efficiency:
- Smart thermostats that adjust based on solar production
- Automated appliances that run during peak solar hours
- Energy management systems that direct power to priority devices
- Smart plugs that control individual devices based on solar availability
- Home automation hubs that coordinate multiple systems
These integrations help you get the most from every watt your system produces.
Smart Energy Management systems can transform how you use solar power. They monitor your production in real-time and automatically adjust your home’s energy use. For example:
- Running the dishwasher or clothes dryer when solar production is highest
- Preheating or precooling your home while solar is abundant
- Charging electric vehicles during peak production
- Reducing phantom loads during low-production periods
Many utility companies now offer special time-of-use rates that make smart energy management even more valuable.
By shifting energy-intensive activities to low-rate periods, you can maximize the financial benefits of your solar system.
Weather Stations
Local weather conditions directly impact solar production.
A personal weather station can:
- Help predict daily energy production
- Alert you to conditions that might affect your system
- Provide data to optimize panel angles and cleaning schedules
- Track historical weather patterns for system performance analysis
- Integrate with smart home systems for coordinated energy management
Many weather stations connect to your home network, making data easily accessible.
Advanced weather stations might include:
- Solar radiation sensors to directly measure available sunlight
- Wind speed and direction indicators to predict cooling effects on panels
- Temperature sensors to monitor both ambient and panel temperatures
- Rain gauges to track when natural cleaning might occur
- Historical data logging for long-term performance analysis
Specialized Accessories for Specific Needs
RV and Portable Solar Accessories
For those on the move, portable solar offers flexibility:
- Foldable solar panels
- Battery packs with built-in inverters
- Quick-connect cables for easy setup and breakdown
- Specialized mounting hardware for RVs, boats, and campers
- Solar generators for all-in-one power solutions
- Waterproof solar blankets for outdoor adventures
These systems prioritize convenience and portability over maximum output.
RV-Specific Solar Solutions include:
- Rooftop installations that don’t require setup at each location
- Combination systems with both fixed and portable components
- Solar-ready prewiring for easier installation
- Solar charge controllers with multiple battery bank options
- Energy-efficient DC appliances that run directly from battery power
For weekend campers, simple portable panels might be sufficient. For full-time RV living, a more comprehensive system with fixed panels and substantial battery storage is often necessary.
Cold Climate Accessories
Solar works in cold climates too, but might need some help:
- Panel heaters to melt snow
- Steeper mounting angles to prevent snow accumulation
- Cold-rated batteries that perform in low temperatures
- Insulated battery enclosures
- Wind deflectors to reduce snow drifting
- Heavy-duty mounting systems to handle snow loads
- Specialized inverters rated for extreme temperatures
These additions ensure year-round performance, even in harsh winter conditions.
Snow Removal Options:
- Passive systems – Special coatings or mounting angles that help snow slide off naturally
- Active systems – Heating elements that melt snow (using a small amount of panel energy)
- Manual tools – Long-handled soft brushes designed specifically for solar panel cleaning
Many cold-climate solar owners are surprised to learn that panels actually operate more efficiently in cold temperatures (as long as they’re not covered in snow).
The challenge isn’t the cold itself, but rather snow accumulation blocking sunlight.
Grid Connection and Safety Equipment
Grid-Tie Equipment
For systems connected to the utility grid, several specific components are essential:
- Grid-tie inverters with anti-islanding protection
- Net meters that track energy sent to and drawn from the grid
- AC disconnects for emergency shutoff
- Surge protection devices to guard against lightning and grid fluctuations
- Transfer switches for systems with battery backup
Grid connection requirements vary by location, so always check local regulations before purchasing equipment.
Safety Equipment
Proper safety equipment protects both your system and the people who interact with it:
- DC disconnects to isolate solar panels during maintenance
- Rapid shutdown systems to quickly de-energize panels (now required by code in many areas)
- Ground fault protection to prevent electrical fires
- Lightning arrestors for exposed installations
- Safety labels and signage to alert emergency responders
- Cable management systems to prevent trips and falls during maintenance
Never compromise on safety equipment, even for small systems. Solar arrays can produce lethal voltage and current levels.

Installation Tips and Safety Considerations
DIY vs. Professional Installation
Some accessories are simple enough for DIY installation, while others require professional help:
DIY-friendly:
- Monitoring systems
- Basic cleaning equipment
- Simple panel angle adjustments
- Some ground-mount systems
- Portable solar setups
- Basic maintenance and inspections
Professional recommended:
- Battery systems
- Main electrical components
- Roof mounting systems
- Grid-tie connections
- Complex inverter replacements
- Any work involving high voltage DC circuits
When in doubt, consult a professional. The safety risks and potential system damage aren’t worth the saved installation costs.
Permitting and Regulations
Before adding significant accessories to your system, check local requirements:
- Building permits may be needed for structural additions
- Electrical permits are typically required for battery systems
- Homeowners associations might have restrictions on visible equipment
- Utility companies often have specific requirements for grid-connected systems
- Insurance companies may need to be notified of system changes
Non-compliance can lead to insurance issues, utility disconnection, or even municipal fines.
Maintaining Your Solar Accessories
Maintenance Schedule
Create a calendar for regular maintenance:
- Monthly:
- Visual inspections
- Check monitoring system for performance issues
- Clear debris from panels and mounting areas
- Quarterly:
- Panel cleaning (more often in dusty areas)
- Check for shading from growing vegetation
- Inspect for loose mountings or connections
- Bi-annually:
- Electrical connection checks
- Battery maintenance (if applicable)
- Inverter cooling system cleaning
- Annually:
- Professional system assessment
- Infrared scanning for hot spots
- Software and firmware updates
- Racking and mounting hardware inspection
Regular maintenance extends equipment life and maintains efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Know the signs of potential problems:
- Unexpected drops in energy production
- Warning lights on inverters or charge controllers
- Unusual noises from electrical components
- Corrosion on connections or mounting hardware
- Discoloration or bubbling on panels
- Error codes on monitoring systems
- Inconsistent battery performance
- Circuit breakers tripping frequently
Early intervention prevents most major issues.
Common Solutions:
- Cleaning dirty panels
- Tightening loose connections
- Updating inverter firmware
- Replacing worn cable glands and weatherproofing
- Applying dielectric grease to connections
- Rebalancing battery banks
- Adjusting charge controller settings
- Clearing ventilation paths around electronics
Keep a log of any issues and solutions for future reference. Patterns can reveal underlying problems that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Looking Forward: Emerging Solar Accessory Trends
The solar accessory market continues to evolve with:
- More affordable battery options
- AI-powered energy management
- Building-integrated solar accessories
- Virtual power plant participation technologies
- Bi-facial panels that capture reflected light
- Solar roof tiles that replace traditional roofing
- DC appliances that run directly from solar without conversion losses
- Vehicle-to-home charging that uses electric car batteries to power homes
- Transparent solar technologies for windows and skylights
- Perovskite panel technologies with higher efficiency
Staying informed about new developments helps you make future-proof purchasing decisions.
Integration with Electric Vehicles
As electric vehicles become more common, integration with home solar systems presents exciting opportunities:
- Using EV batteries as home backup power
- Smart charging systems that prioritize solar power
- Bi-directional chargers that allow power flow in both directions
- Energy management systems that balance home, car, and grid needs
- Mobile apps that coordinate charging based on solar production forecasts
Many experts see the future of residential energy as a seamless ecosystem of solar production, home consumption, vehicle charging, and grid interaction, all managed by smart systems that optimize for both cost and environmental impact.
Financial Considerations and Incentives
Incentives for Solar Accessories
Many regions offer incentives specifically for solar accessories:
- Battery storage tax credits or rebates
- Smart energy management system rebates
- Utility company incentives for grid-supporting technologies
- Property tax exemptions for renewable energy improvements
- Low-interest financing for energy efficiency upgrades
Check with local energy offices, utility companies, and tax professionals to identify available incentives.
Warranty Considerations
Different components typically carry different warranty terms:
- Panels: 25-30 year production warranty, 10-12 year product warranty
- Inverters: 5-10 years (25 for some microinverters)
- Batteries: 5-15 years or cycle-based
- Mounting hardware: 10-25 years
- Monitoring systems: 2-5 years
When purchasing accessories, compare not just the warranty length but also what’s covered. Some warranties only cover materials, while others include labor costs for replacement.
Conclusion
The right solar accessories transform a basic solar panel system into a comprehensive energy solution tailored to your specific needs. For a complete solar accessories guide: everything you need, you’ll want to understand the options available and carefully select additions that complement your system to maximize both performance and longevity.
By understanding the options available and carefully selecting additions that complement your system, you’ll maximize both performance and longevity.
Solar technology continues to advance rapidly, offering more efficient, affordable, and integrated options each year.
Whether you’re looking to expand an existing system or planning a new installation, the accessories you choose play a crucial role in determining your overall satisfaction and return on investment.